VoIP Overview
The Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) was introduced to utilize the internet for telephony applications. Internet protocols have been in widespread use for the last 20-30 years. Opportunities arose to use them for commercial and multimedia services. VoIP is a general term for a family of network transport technologies for delivery of voice communications over IP networks. A simple model of VoIP comprises one or more VoIP servers that function as a switchboard and a number of VoIP clients (typically handsets) to make or receive calls.
The standard VoIP platform comprises telephony servers, handsets and network components, IP connectivity, telephony software and optional ISDN connectivity.
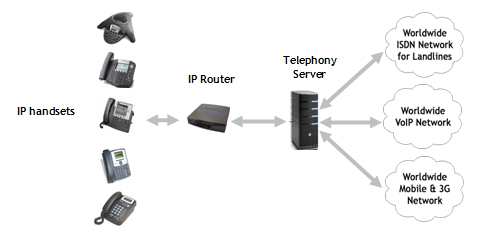
Telephony Servers:
The telephony servers act as the VoIP telephone switchboards and can be hosted internally, i.e. inside the customers premises or externally in a data centre.
IP Handsets:
The platform includes industry standard VoIP handsets from leading manufacturers such as Polycom, CISCO and Linksys. These handsets are similar to the traditional phones and work like a small computer with a large number of flexible call handling features.
Network infrastructure:
The platform also comprises standard network infrastructure including IP router, a network switch and Category 5e/6 cabling.
VoIP connectivity:
There are several other ways of providing IP connectivity. Leased line (e.g. MPLS) provides a dedicated connection between the customer premises and the data centre. Connectivity can also be achieved through ADSL or SDSL (Asymmetric or Symmetric Digital Subscribers Line) broadband. SDSL is now being increasingly used by businesses because of the enhanced reliability it offers over ADSL. VOIPLEX has developed partnerships with various IP connectivity providers ensuring a secure and reliable communication service for businesses.